Typically, we spend a major period of time attempting to grasp blocks of code, comprehend the parameters, and decipher different complicated elements of the code. I believed to myself, can the much-hyped AI Brokers assist me on this regard? The system that I have been to create had a transparent goal: to supply useful feedback, flags on duplicate variables, and, extra importantly, check features to see the pattern outputs myself. This seems to be very a lot attainable, proper? Let’s design this Agentic system utilizing the favored LangGraph framework.
LangGraph for Brokers
LangGraph, constructed on prime of LangChain, is a framework that’s used to create and orchestrate AI Brokers utilizing stateful graphs (state is a shared information construction used within the workflow). The graph consists of nodes, edges, and states. We’ll not delve into advanced workflows; we’ll create a easy workflow for this challenge. LangGraph helps a number of LLM suppliers like OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, and so forth. Notice that I’ll be sticking to Gemini on this information. Instruments are an vital asset for Brokers that assist them lengthen their capabilities. What’s an AI Agent, you ask? AI Brokers are LLM-powered, which might motive or assume to make selections and use instruments to finish the duty. Now let’s proceed to designing the move and coding the system.
Workflow of the system
The aim of our system might be so as to add documentation strings for features and flag any points as feedback within the code. Additionally, to make this method smarter, we’ll verify if the feedback exist already to skip including the identical utilizing the agentic system. Now, let’s take a look at the workflow I’ll be utilizing and delve into it.
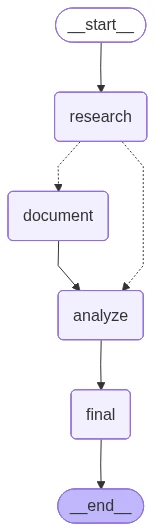
So, as you may see, we’ve got a analysis node which is able to use an agent that may take a look at the enter code and likewise “motive” if there’s documentation already current. It’ll then use conditional routing utilizing the ‘state’ to resolve the place to go subsequent. First, the documentation step writes the code primarily based on the context that the analysis node offers. Then, the evaluation node checks the code on a number of check instances utilizing the shared context. Lastly, the final node saves the knowledge in evaluation.txt and shops the documented code in code.py.
Coding the Agentic system
Pre-requisites
We are going to want the Gemini API Key to entry the Gemini fashions to energy the agentic system, and likewise the Tavily API Key for internet search. Ensure you get your keys from the hyperlinks under:
Gemini: https://aistudio.google.com/apikey
Tavily: https://app.tavily.com/house
For simpler use, I’ve added the repository to GitHub, which you’ll clone and use:
https://github.com/bv-mounish-reddy/Self-Documenting-Agentic-System.git
Be certain that to create a .env file and add your API keys:
GOOGLE_API_KEY=
TAVILY_API_KEY=I used the gemini-2.5-flash all through the system (which is free to an extent) and used a few instruments to construct the system.
Device Definitions
In LangGraph, we use the @software decorator to specify that the code/operate might be used as a software. We’ve outlined these instruments within the code:
# Instruments Definition
@software
def search_library_info(library_name: str) -> str:
"""Seek for library documentation and utilization examples"""
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=2)
question = f"{library_name} python library documentation examples"
outcomes = search_tool.invoke(question)
formatted_results = []
for end in outcomes:
content material = end result.get('content material', 'No content material')[:200]
formatted_results.append(f"Supply: {end result.get('url', 'N/A')}nContent: {content material}...")
return "n---n".be part of(formatted_results)This software is utilized by the analysis agent to grasp the syntax related to the Python libraries used within the enter code and see examples of the way it’s getting used.
@software
def execute_code(code: str) -> str:
"""Execute Python code and return outcomes"""
python_tool = PythonREPLTool()
strive:
end result = python_tool.invoke(code)
return f"Execution profitable:n{end result}"
besides Exception as e:
return f"Execution failed:n{str(e)}"This software executes the code with the inputs outlined by the evaluation agent to confirm whether or not the code works as anticipated and to verify for any loopholes.
Notice: These features are outlined utilizing the inbuilt LangGraph instruments: PythonREPLTool() and TavilySearchResults().
State Definition
The shared information within the system must have a transparent construction to create a very good workflow. I’m creating the construction as a TypedDict with the variables I’ll be utilizing within the agentic system. The variables will present context to the next nodes and likewise assist with the routing within the agentic system:
# Simplified State Definition
class CodeState(TypedDict):
"""Simplified state for the workflow"""
original_code: str
documented_code: str
has_documentation: bool
libraries_used: Record[str]
research_analysis: str
test_results: Record[str]
issues_found: Record[str]
current_step: strAgent Definitions
We used a ReAct (reasoning and appearing) type agent for the ‘Analysis Agent’, which must be taught and motive. A ReAct-style agent can merely be outlined utilizing create_react_agent operate by passing the parameters, and this agent might be used within the node. Discover that we’re passing the beforehand outlined software within the create_react_agent operate. The node utilizing this Agent additionally updates a number of the state variables, which might be handed as context.
# Initialize Mannequin
def create_model():
"""Create the language mannequin"""
return ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(
mannequin="gemini-2.5-flash",
temperature=0.3,
google_api_key=os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"]
)
# Workflow Nodes
def research_node(state: CodeState) -> CodeState:
"""
Analysis node: Perceive code and verify documentation
Makes use of agent with search software for library analysis
"""
print("RESEARCH: Analyzing code construction and documentation...")
mannequin = create_model()
research_agent = create_react_agent(
mannequin=mannequin,
instruments=[search_library_info],
immediate=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", PROMPTS["research_prompt"]),
("placeholder", "{messages}")
])
)
# Analyze the code
analysis_input = {
"messages": [HumanMessage(content=f"Analyze this Python code:nn{state['original_code']}")]
}
end result = research_agent.invoke(analysis_input)
research_analysis = end result["messages"][-1].content material
# Extract libraries utilizing AST
libraries = []
strive:
tree = ast.parse(state['original_code'])
for node in ast.stroll(tree):
if isinstance(node, ast.Import):
for alias in node.names:
libraries.append(alias.identify)
elif isinstance(node, ast.ImportFrom):
module = node.module or ""
for alias in node.names:
libraries.append(f"{module}.{alias.identify}")
besides:
go
# Examine if code has documentation
has_docs = ('"""' in state['original_code'] or
"'''" in state['original_code'] or
'#' in state['original_code'])
print(f" - Libraries discovered: {libraries}")
print(f" - Documentation current: {has_docs}")
return {
**state,
"libraries_used": libraries,
"has_documentation": has_docs,
"research_analysis": research_analysis,
"current_step": "researched"
}Equally, we outline the opposite brokers as properly for the nodes and tweak the prompts as wanted. We then proceed to outline the sides and workflow as properly. Additionally, discover that has_documents variable is important for the conditional routing within the workflow.
Outputs
You’ll be able to change the code in the primary operate and check the outcomes for your self. Right here’s a pattern of the identical:
Enter code
sample_code = """
import math
import random
def calculate_area(form, **kwargs):
if form == "circle":
return math.pi * kwargs["radius"] ** 2
elif form == "rectangle":
return kwargs["width"] * kwargs["height"]
else:
return 0
def divide_numbers(a, b):
return a / b
def process_list(objects):
whole = 0
for i in vary(len(objects)):
whole += objects[i] * 2
return whole
class Calculator:
def __init__(self):
self.historical past = []
def add(self, a, b):
end result = a + b
self.historical past.append(f"{a} + {b} = {end result}")
return end result
def divide(self, a, b):
return divide_numbers(a, b)
calc = Calculator()
end result = calc.add(5, 3)
space = calculate_area("circle", radius=5)
division = calc.divide(10, 2)
objects = [1, 2, 3, 4]
processed = process_list(objects)
print(f"Outcomes: {end result}, {space:.2f}, {division}, {processed}")
"""Pattern Output
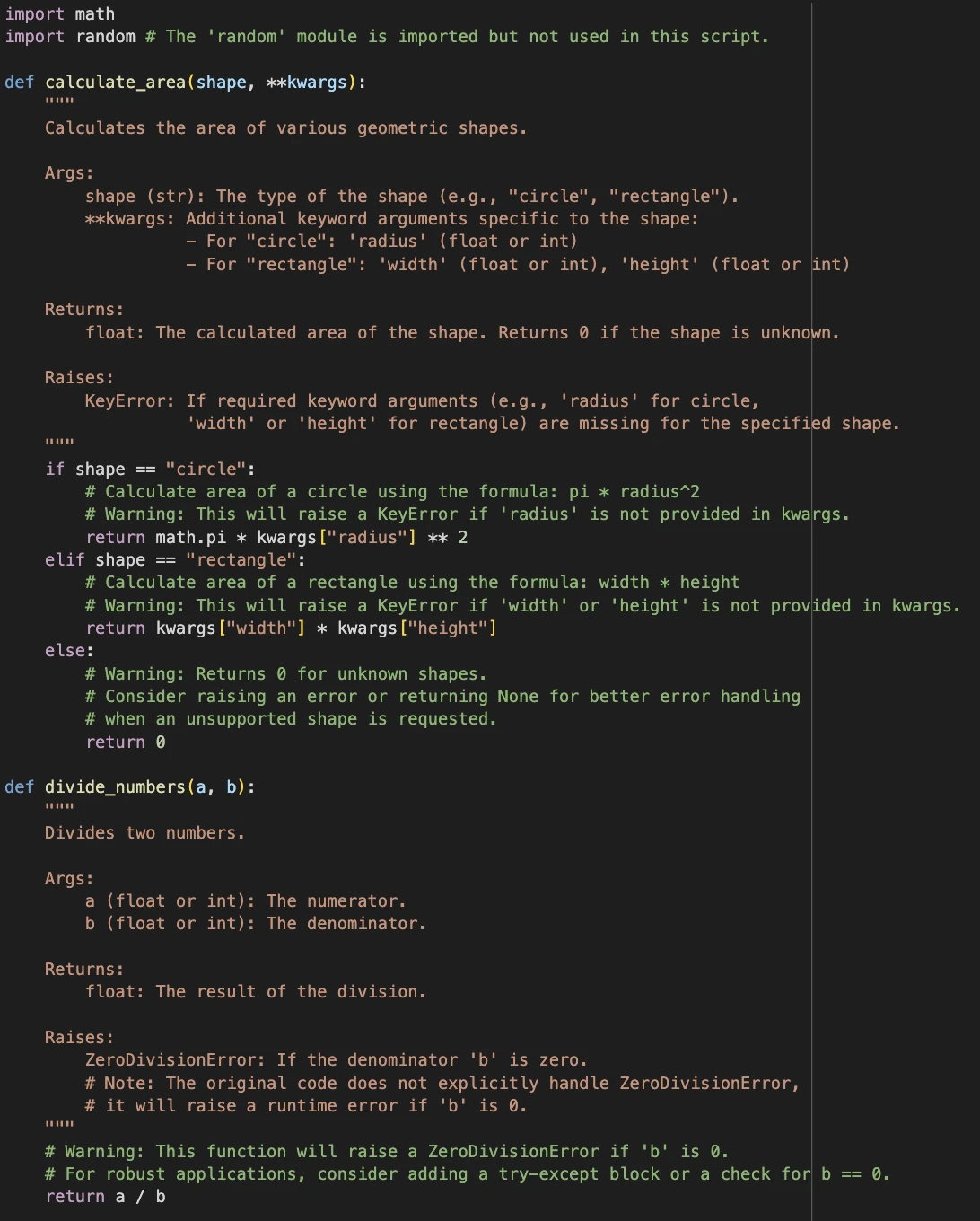
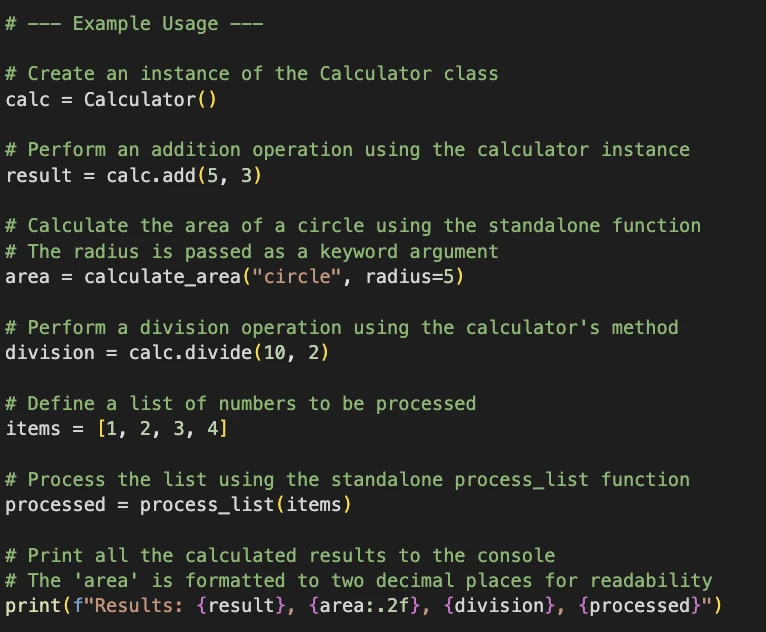
Discover how the system says the random module is imported however not used. The system provides docstrings, flags points, and likewise provides feedback within the code about how the features are getting used.
Conclusion
We constructed a easy agentic system with the usage of LangGraph and understood the significance of state, instruments, and brokers. The above system may be improved with the usage of further nodes, instruments, and refinements within the prompts. This technique may be prolonged to constructing a debugging system or a repository builder as properly, with the correct nodes and instruments. Additionally, keep in mind that utilizing a number of brokers will even end in greater prices when utilizing a paid mannequin, so create and use brokers that add worth to your agentic techniques and outline the workflows properly prematurely.
Incessantly Requested Questions
A. It’s the way you mark a operate so a LangGraph agent can name it as a software inside workflows.
A. It’s the loop the place brokers motive step-by-step, act with instruments, then observe outcomes.
A. Yeah, you may plug it into audits, debugging, compliance, and even reside information bases. Code documentation is without doubt one of the use instances.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.

